What is a automatic wire stripping machine used for?
1. The main application areas of wire harness processing
Automotive industry: Every electrical component in a car needs to be connected through a wire harness, such as engine control, lighting, air conditioning, etc. Therefore, wire harness processing is an important link in the automotive industry.
Electronic equipment industry: The connection between various circuit boards in electronic equipment also needs to be achieved through wire harnesses, such as mobile phones, computers, etc.
Aerospace field: In the aerospace field, wire harnesses are an important connection method between electrical equipment, and the requirements for safety are extremely high, so the process and quality of its wire harness processing are also extremely high.
Industrial automation: In the field of industrial automation, wire harness connection is an important part of various mechanical equipment and control systems, such as robots, production lines, etc.
Home appliance industry: Motor control, power connection, etc. in home appliances require wire harness processing.

 2. The importance of wire harness processing in modern manufacturing
2. The importance of wire harness processing in modern manufacturing
In modern manufacturing, wire harnesses are the key connecting bridges between electronic components, modules, and systems. Whether it is automobiles, aerospace, communication equipment or electronic equipment, accurate and correct wire harness connections are required to ensure the normal operation of equipment functions. Any errors or failures in wire harness connection may paralyze the entire system. Therefore, the quality and accuracy of wire harness processing are directly related to the production efficiency and product quality of modern manufacturing industry.
With the improvement of production automation level, the efficiency and accuracy of wire harness processing play a vital role in improving production efficiency. Automation and intelligent technologies in wire harness processing, such as automation equipment, intelligent detection systems, etc., can greatly improve production efficiency and reduce errors and costs of manual operation. At the same time, efficient wire harness processing process can shorten the production cycle and speed up the product launch, so as to meet the rapidly changing needs of the market.
For many products, especially those involving life safety or important functions, such as automobiles and medical equipment, the safety of wire harness is crucial. Any short circuit, open circuit or poor contact of the wire harness may lead to serious consequences. Therefore, high-quality wire harness processing is an important link to ensure product safety. In the production process, strict quality control, material selection and testing processes are key steps to ensure product safety.
In the fierce market competition, product quality and performance are important factors to win the market. High-quality and high-precision wire harness processing can improve the overall performance of the product and make it stand out from similar products. In addition, through the continuous optimization and innovation of wire harness processing, personalized customization and differentiated competition of products can be achieved, thereby improving the market competitiveness of products.
The importance of wire harness processing in modern manufacturing is self-evident. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous improvement of market demand, the status and role of wire harness processing will become more and more prominent. Therefore, mastering the basic knowledge of wire harness processing and improving the technical level and production efficiency of wire harness processing are of great significance to the development of modern manufacturing.
3. Application scenarios of automatic wire stripping machine
(1) Single-core wire stripping machine: focusing on the precision processing of fine-diameter cables
Core adaptation objects: single-strand insulated cables with a diameter of 0.1mm-2mm, such as internal connecting wires of electronic equipment, sensor leads, enameled wires, etc.
Technical features: Use micro-tools (such as ceramic blades) to avoid damage to fine-core wires (copper wire diameter is often less than 0.05mm);
The stripping length accuracy can be controlled at ±0.05mm, meeting the miniaturized assembly requirements of electronic components;
Support "half stripping" (stripping only part of the insulation layer) and "full stripping" modes, suitable for PCB board welding, terminal plug-in and other scenarios.
Typical application areas:
Consumer electronics: internal thin cable processing of mobile phones and headphones;
Electronic components: stripping of resistors and capacitors;
Precision instruments: pre-processing of test lines for multimeters and oscilloscopes.
(2)Multi-core cable stripping machine: batch processing of large-diameter multi-strand cables
Core adaptation objects: multi-strand twisted cables with a diameter of 2mm-50mm, such as power cables, communication cables (network cables, coaxial cables), automotive wiring harnesses, etc.
Technical features:
Equipped with a high-power wire feeding mechanism, it can drive large-diameter cables to feed stably;
Support "layered wire stripping": first strip the outer sheath, and then strip the insulation layer of each inner core wire separately (such as the 8 core wires of the network cable are processed simultaneously);
Integrated waste separation device to classify and collect the sheath and core wire insulation for easy recycling.
Typical application areas:
Electric power industry: terminal stripping of low-voltage cables (0.4kV);
Communication industry: outer sheath stripping of optical fiber cables, and whole-section stripping of network cables;
Automobile manufacturing: centralized processing of multi-core wire harnesses in the engine compartment of automobiles.
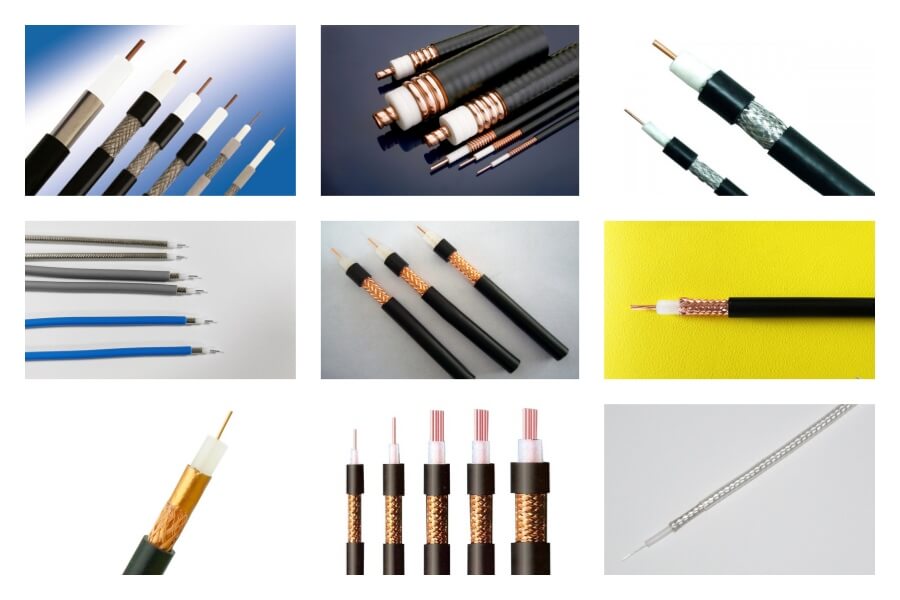
(3)Special cable stripping machine: to meet the customized needs of special materials and structures
Core adaptation objects: cables with special insulating materials or complex structures, such as high-temperature wires (resistant to more than 200℃), shielded wires (including metal braided layers), coaxial cables (including aluminum foil shielding layers), silicone wires, Teflon wires, etc.
Technical features:
The tool has strong adaptability: tungsten steel tools are used for high-temperature materials (such as polyimide), and blunt blade cutting is used for soft materials (such as silicone) to avoid adhesion;
Integrated auxiliary processing functions: such as the integration of "stripping the jacket + cutting the shielding layer" of the shielded cable, and the step-by-step operation of "stripping the outer layer + stripping the insulation layer + exposing the core wire" of the coaxial cable;
Equipped with a tension adaptive system to prevent elastic material cables (such as silicone wires) from stretching and deforming during stripping.
(4)Typical application areas:
Industrial equipment: stripping of sensor cables (such as kiln temperature measurement cables) in high-temperature environments;
Military industry and aerospace: processing of special cables that are resistant to radiation and aging;
Medical equipment: stripping of silicone monitor connection cables (must meet the requirement of no debris residue).
The core difference between the three types of equipment lies in their adaptability to cable specifications and material properties: single-core wire stripping machines pursue "precision", multi-core cable stripping machines focus on "batch and strength", and special cable stripping machines focus on "compatibility in special scenarios", covering all scenarios from micro electronic wires to large industrial cables.
 4. Core components and workflow of automatic wire stripping machine
4. Core components and workflow of automatic wire stripping machine
1. Key hardware components
Wire feeding mechanism: precisely control the cable feeding length
Wire stripping tool: blade material (such as tungsten steel, ceramic) and cutting angle design
Tension adjustment system: avoid cable pulling and deformation
Waste collection device: improve the cleanliness of the processing environment
2. Standardized workflow
Cable feeding and fixing
Parameter setting (stripping length, stripping depth)
Tool positioning and cutting execution
Insulation separation and waste treatment
Finished product collection and quality inspection
 5. Technical advantages of automatic wire stripping machine
5. Technical advantages of automatic wire stripping machine
(1)Efficiency improvement: the leap from "manual rhythm" to "machine speed"
Quantitative comparison: manual wire stripping is limited by physical strength and proficiency, and the daily production capacity of a single person is about 500-2000 wires (depending on the wire diameter); the automatic wire stripping machine can achieve a daily production capacity of 5000-20000 wires through continuous operation, and the efficiency is improved by 5-10 times.
Batch adaptability: supports continuous loading and multi-station parallel processing (such as stripping multiple cables at the same time), especially suitable for "large-scale, standardized" production scenarios such as automotive wiring harnesses and electronic processing.
Time utilization: no need for manual rest, it can cooperate with the production line to achieve 24-hour uninterrupted operation, only regular replenishment of raw materials and maintenance are required, which greatly improves the equipment utilization rate.
(2)Precision control: a breakthrough from millimeter-level error to micron-level precision
Core parameters: The stripping length error can be stably controlled within ±0.1mm, and some high-end CNC models can even reach ±0.05mm, far exceeding the ±1-3mm error range of manual operation.
Consistency guarantee: through the program preset parameters (stripping length, stripping depth, cutting force), ensure that the processing effect of each cable is completely consistent, avoiding quality fluctuations caused by fatigue and experience differences in manual operation.
Complex process adaptation: supports fine operations such as "segmented stripping" (such as different stripping lengths at both ends of the cable) and "half stripping" (stripping only part of the insulation layer and retaining the middle connection section) to meet the high-precision requirements of electronic component welding, terminal crimping, etc.
(3)Material protection: Upgrading from "extensive stripping" to "non-destructive processing"
Prevention of core wire damage: Manual stripping often causes copper core breakage, scratches or oxidation (especially thin core wires below 0.1mm) due to uneven force of the tool. The automatic wire stripping machine uses a tension adaptive system and a blunt blade cutting design to ensure that the core wire is not stressed and damaged when the insulation layer is stripped.
Insulation layer integrity: Avoid residual, broken or deformed insulation layer caused by manual tearing, especially for tough materials such as Teflon and silicone, which can achieve a "smooth cut and burr-free" stripping effect.
Special material adaptation: For easily damaged materials such as high-temperature wires and shielded wires, customized tools (such as ceramic knives, high-temperature alloy knives) and ultrasonic stripping technology are used to not destroy the original properties of the material (such as temperature resistance and shielding effect) during the stripping process.
(4)Cost optimization: transformation from "short-term manpower" to "long-term cost reduction"
Manpower cost savings: one automatic wire stripping machine can replace 3-5 workers. Based on an average monthly salary of 5,000 yuan per person, the equipment investment (about 10,000-100,000 yuan, depending on the model) can be recovered within 6-18 months, and the long-term use cost is significantly lower than that of labor.
Reduced material loss: the high error rate of manual operation often leads to the scrapping of cables (such as the wire stripping is too short and needs to be cut off and re-stripped). The precise control of the automatic wire stripping machine can reduce the material loss rate from 5%-10% to less than 1%, especially for precious metal cables (such as silver-plated wires and optical fibers). The saving effect is more significant.
Reduced management costs: There is no need to invest extra energy in manual training, scheduling, work-related injury risks, etc. The equipment can achieve remote monitoring and fault warning through a digital system, reducing management complexity.
 EC-6100 Automatic Heat Shrink Tube Cutting Machine EC-6800 Automatic Cutting Machine EC-6100H Automatic Hot Cutting Machine EC-830 Corrugated Tube Cutting Machine EC-6500 Automatic Cable and Tube Cutting Machine EC-810 Automatic Cable Cutting Machine EC-850X Automatic Rotary Cutting Machine EC-821 Corrugated Tube Cutting Machine EC-890 Multifunctional Automatic Cutting Machine EC-870 High-power Automatic Tube Cutting Machine EC-816 Automatic Cutting Machine EC-823 High Speed Cutting Machine EC-805 Automatic Cable Cutting Machine EC-860 Corrugated Tube Cutting Machine EC-830F Automatic Tube Cutting Machine With Feeding System EC-830FS Tube Cutting Machine With Feeding System EC-3100 Automatic Cable and Tube Cutting Machine
EC-6100 Automatic Heat Shrink Tube Cutting Machine EC-6800 Automatic Cutting Machine EC-6100H Automatic Hot Cutting Machine EC-830 Corrugated Tube Cutting Machine EC-6500 Automatic Cable and Tube Cutting Machine EC-810 Automatic Cable Cutting Machine EC-850X Automatic Rotary Cutting Machine EC-821 Corrugated Tube Cutting Machine EC-890 Multifunctional Automatic Cutting Machine EC-870 High-power Automatic Tube Cutting Machine EC-816 Automatic Cutting Machine EC-823 High Speed Cutting Machine EC-805 Automatic Cable Cutting Machine EC-860 Corrugated Tube Cutting Machine EC-830F Automatic Tube Cutting Machine With Feeding System EC-830FS Tube Cutting Machine With Feeding System EC-3100 Automatic Cable and Tube Cutting Machine CS-4507/6010 Multifunctional Wire Stripping Machine UniStrip 2016 Pneumatic Wire Stripping Machine UniStrip 2018E Electric Cable Wire Stripping Machine CS-5507 Automatic coaxial cable stripping machine CS-5515 Automatic coaxial cable stripping machine CS-400 Braided Shield Cable Stripping Machine CS Series Rotary Cable Stripping Machine CS-2486 Coaxial Cable Wire Stripping Machine
CS-4507/6010 Multifunctional Wire Stripping Machine UniStrip 2016 Pneumatic Wire Stripping Machine UniStrip 2018E Electric Cable Wire Stripping Machine CS-5507 Automatic coaxial cable stripping machine CS-5515 Automatic coaxial cable stripping machine CS-400 Braided Shield Cable Stripping Machine CS Series Rotary Cable Stripping Machine CS-2486 Coaxial Cable Wire Stripping Machine TM-20 Terminal Crimping Machine TM-20S Automatic Wire Terminal Crimping Machine TM-200 Terminal Crimping Machine TM-10P Registered Jack Crimping Machine TM-E140 Pre-insulation Ferrule Terminal Strip And Crimp Machine TM-E140S Automatic Wire Stripping Ferrule Crimping Machine TM-P300 Pneumatic Terminal Crimping Machine TM-E116 Electric Terminal Crimping Machine TM-P120 Pneumatic Terminal Crimping Machine SAT-AS6P Pneumatic Crimping Applicator SAT-MS6 Mechanical Crimping Applicator Side Feed Terminal Crimping Applicator Rear Feed Terminal Crimping Applicator Flag Terminal Crimping Applicator Crimp Applicator for Insulated Terminals TM-T Series Intelligent Servo Terminal Crimping Machine SAT-MS5 OTP Mechanical Applicator TM-25M Automatic Terminal Crimping Machine TM-FK40 Terminal Crimping Machine TM-CS6 Ultra Silent Copper Belt Crimping Machine
TM-20 Terminal Crimping Machine TM-20S Automatic Wire Terminal Crimping Machine TM-200 Terminal Crimping Machine TM-10P Registered Jack Crimping Machine TM-E140 Pre-insulation Ferrule Terminal Strip And Crimp Machine TM-E140S Automatic Wire Stripping Ferrule Crimping Machine TM-P300 Pneumatic Terminal Crimping Machine TM-E116 Electric Terminal Crimping Machine TM-P120 Pneumatic Terminal Crimping Machine SAT-AS6P Pneumatic Crimping Applicator SAT-MS6 Mechanical Crimping Applicator Side Feed Terminal Crimping Applicator Rear Feed Terminal Crimping Applicator Flag Terminal Crimping Applicator Crimp Applicator for Insulated Terminals TM-T Series Intelligent Servo Terminal Crimping Machine SAT-MS5 OTP Mechanical Applicator TM-25M Automatic Terminal Crimping Machine TM-FK40 Terminal Crimping Machine TM-CS6 Ultra Silent Copper Belt Crimping Machine ESC-BX1 Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX4 Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX30 Automatic Large Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX30S Sheathed Cable Automatic Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BXR Automatic Rotary Cable Stripping Machine ESC-BX6 Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX7 Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX8S Sheath Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX8PR Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX9 Automatic Cut and Strip Machine ESC-BX30SC Automatic Cable Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX120 Automatic Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX30RS Multi-function Rotary Cable Stripping Machine ESC-BX120S Multi-core Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX60 Automatic Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine CS-9580 Automatic Coaxial Cable Stripping Machine CS-9680 Automatic Coaxial Cable Stripping Machine ESC-BX300 Automatic Cable Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX16 Wire Cutting Stripping Machine ESC-BX20SF Flat Twin Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine
ESC-BX1 Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX4 Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX30 Automatic Large Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX30S Sheathed Cable Automatic Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BXR Automatic Rotary Cable Stripping Machine ESC-BX6 Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX7 Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX8S Sheath Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX8PR Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX9 Automatic Cut and Strip Machine ESC-BX30SC Automatic Cable Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX120 Automatic Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX30RS Multi-function Rotary Cable Stripping Machine ESC-BX120S Multi-core Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine ESC-BX60 Automatic Cable Cutting and Stripping Machine CS-9580 Automatic Coaxial Cable Stripping Machine CS-9680 Automatic Coaxial Cable Stripping Machine ESC-BX300 Automatic Cable Wire Cutting And Stripping Machine ESC-BX16 Wire Cutting Stripping Machine ESC-BX20SF Flat Twin Wire Cutting and Stripping Machine TM-200SC Automatic Strip and Weather Pack Terminal Crimp Machine TM-20SCM Automatic Cable Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-80SCS Servo Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-30SC Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-15SCE Electric Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-20SCS Servo Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-15SC Stripping and Crimping Machine
TM-200SC Automatic Strip and Weather Pack Terminal Crimp Machine TM-20SCM Automatic Cable Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-80SCS Servo Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-30SC Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-15SCE Electric Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-20SCS Servo Stripping and Crimping Machine TM-15SC Stripping and Crimping Machine ACC-101 Automatic Single-head Terminal Crimping Machine ACC-102A Fully Automatic Terminal Crimping Machine (Both Ends) ACC-102B Automatic Double Terminal Crimping Machine ACC-105 Fully Automatic Single-head End-dipping Tin Machine ACC-106 Fully Automatic 5-Wire Single-head End-dipping Tin Machine ACC-202UP Fully-automatic cut,strip,crimp,insert and Heat Heat-shrink tube machine ACC-308 (Both ends) Full automatic Soldering machine ACC-208 Fully Automatic Crimping Machine (Both Ends) ACC-508 Fully Automatic Twisting, Soldering and Crimping Machine ACC-608 Fully Automatic Flat Cable Cut Strip and Crimp Machine
ACC-101 Automatic Single-head Terminal Crimping Machine ACC-102A Fully Automatic Terminal Crimping Machine (Both Ends) ACC-102B Automatic Double Terminal Crimping Machine ACC-105 Fully Automatic Single-head End-dipping Tin Machine ACC-106 Fully Automatic 5-Wire Single-head End-dipping Tin Machine ACC-202UP Fully-automatic cut,strip,crimp,insert and Heat Heat-shrink tube machine ACC-308 (Both ends) Full automatic Soldering machine ACC-208 Fully Automatic Crimping Machine (Both Ends) ACC-508 Fully Automatic Twisting, Soldering and Crimping Machine ACC-608 Fully Automatic Flat Cable Cut Strip and Crimp Machine HSM-60 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-70 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-80B Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-90 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-25M Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-120 Heat Shrink Tube Heating Machine HSM-50 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-160 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-80A Heat Shrink Tube Heating Machine HSM-260E Enclosed Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-260O Open Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-20 Intelligent Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine
HSM-60 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-70 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-80B Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-90 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-25M Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-120 Heat Shrink Tube Heating Machine HSM-50 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-160 Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-80A Heat Shrink Tube Heating Machine HSM-260E Enclosed Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-260O Open Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HSM-20 Intelligent Heat Shrink Tube Processing Machine HV-CS 9070 High-Voltage Cable Shield Cutting Machine HV-FS 9053 Cable Shield Folding Machine HV-ACS 9100 Cable Shield Processing Machine HV-ACS 9200 Automatic Cable Shield Processing System HV-ACS 9300 Automotive High Voltage Cable Processing Machine HV-ACS 9500 High Voltage Cable Processing Machine HV-FC 9312 Aluminum Foil Cutting Machine HV-CS 9120 Cable Stripping Machine
HV-CS 9070 High-Voltage Cable Shield Cutting Machine HV-FS 9053 Cable Shield Folding Machine HV-ACS 9100 Cable Shield Processing Machine HV-ACS 9200 Automatic Cable Shield Processing System HV-ACS 9300 Automotive High Voltage Cable Processing Machine HV-ACS 9500 High Voltage Cable Processing Machine HV-FC 9312 Aluminum Foil Cutting Machine HV-CS 9120 Cable Stripping Machine STB-10 Automatic Tape Bundling Machine STB-50 Desktop Bundling Machine STB-60 Adhesive Tape Bundling Machine STB-55 Desktop Tape Bundling Machine STB-50C Automatic Tape Cutting Machine STP-B Hand-held Taping Machine STP-F Hand-held Lithium Battery Tape Wrapping Machine STP-C Automatic Wire Taping Machine STP-D Automatic Tape Wrapping Machine STP-AS Automatic Tape bundling Machine
STB-10 Automatic Tape Bundling Machine STB-50 Desktop Bundling Machine STB-60 Adhesive Tape Bundling Machine STB-55 Desktop Tape Bundling Machine STB-50C Automatic Tape Cutting Machine STP-B Hand-held Taping Machine STP-F Hand-held Lithium Battery Tape Wrapping Machine STP-C Automatic Wire Taping Machine STP-D Automatic Tape Wrapping Machine STP-AS Automatic Tape bundling Machine CB-B15 Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-BT15 Automatic Wiring Winding Binding Machine CB-F30/150MCS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-F30/150MCST18-45 Automatic Wiring Winding Binding Machine CB-F30/150MCST40-80 Automatic Wiring Winding Binding Machine CB-B15CST Automatic Wiring Coiling Binding Machine CB-F500MCS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-B30/150CS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-B10/15CS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-WT630 Automatic Wire Winding and Tying Machine
CB-B15 Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-BT15 Automatic Wiring Winding Binding Machine CB-F30/150MCS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-F30/150MCST18-45 Automatic Wiring Winding Binding Machine CB-F30/150MCST40-80 Automatic Wiring Winding Binding Machine CB-B15CST Automatic Wiring Coiling Binding Machine CB-F500MCS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-B30/150CS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-B10/15CS Automatic Wiring Winding Machine CB-WT630 Automatic Wire Winding and Tying Machine PF-08 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-30 Automatic Prefeeding Machine PF-60 Automatic Prefeeding Machine PF-150 Automatic Wire Prefeeding Machine CC-380 Cable Coiling Machine CC-680 Automatic Cable Coiling Machine CC-380D Cable Coil Machine PF-120 Large Automatic Wire Prefeeding Machine PF-90 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-100 Automatic Prefeeder PF-04 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-06 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-05 Automatic Wire Prefeeder
PF-08 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-30 Automatic Prefeeding Machine PF-60 Automatic Prefeeding Machine PF-150 Automatic Wire Prefeeding Machine CC-380 Cable Coiling Machine CC-680 Automatic Cable Coiling Machine CC-380D Cable Coil Machine PF-120 Large Automatic Wire Prefeeding Machine PF-90 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-100 Automatic Prefeeder PF-04 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-06 Automatic Wire Prefeeder PF-05 Automatic Wire Prefeeder
 CHM-10 Crimp-Height Measurer PFM-220 Terminal Pulling Force Tester PFM-300 Terminal Pulling Force Tester PFM-200 Pull Force Tester For Wire Terminals TCA-120 Terminal Cross Section Analyzer TCA-120S Terminal Cross Section Analyzer TCA-150 Terminal Cross Section Analyzer PFM-50 Pull Force Measuring Machine
CHM-10 Crimp-Height Measurer PFM-220 Terminal Pulling Force Tester PFM-300 Terminal Pulling Force Tester PFM-200 Pull Force Tester For Wire Terminals TCA-120 Terminal Cross Section Analyzer TCA-120S Terminal Cross Section Analyzer TCA-150 Terminal Cross Section Analyzer PFM-50 Pull Force Measuring Machine





